3D Virtual Rig Tour
3D Virtual Rig Tour
3D Oil Rig Tour Video Animation | John Perez Graphics – Federal Copyright # PA 1-901-682
Crown Block: A device comprised of sheaves or pulleys at the top of the mast over which drilling line is run down to the hoisting drum.
Derrick Board: A platform near the top of the mast on which the derrick man works. Also called a monkey board.
Mast: A portable metal tower that is raised into working position as a unit, rather than assembled as a derrick. A mast is used as a component of the hoisting system of a drilling rig.
Traveling Block: An arrangement of pulleys or sheaves suspended in a derrick with wire rope and used to raise and lower equipment in the well.
Top Drive: A power swivel which rotates the drill string without the use of a rotary table or kelly. It is efficient due to its ability to drill three joints deep before another connection must be added.
Standpipe: A seamless vertical steel pipe attached to one leg of the mast which carries drilling mud up to the rotary hose and swivel.
Driller’s Console: A control panel on the drilling floor used to monitor drilling operations such as weight, speed, pressure, and torque.
Rotary Table: A motorized, circular platform in the floor of the rig which rotates the kelly bushing and the kelly when the top drive is not in use. Turning the kelly turns all the pipe, therefore drilling the hole.
Mousehole: A hole in the drilling floor, seven to ten inches wide, located near the rotary table. It is used to store a piece of drill pipe until it is pulled up and attached to the drill string.
Draw Works: A large winch located on the drilling floor which uses steel wire rope to raise and lower the drilling equipment in the well.
Iron Roughneck: A hydraulic powered wrench which can make up or break out pipe joints by applying correct torque. Most of the manual pipe handling operations previously performed by the drilling crew on the rig floor have been replaced by this piece of equipment.
BOP Controller: A control panel on the drilling floor which can remotely and independently operate each preventer on the BOP stack.
Hydraulic Hoist: Also known as an air hoist. A small cable crane that lifts pipe and equipment up the V door. Also used to hoist personnel for maintenance and repairs on the top drive.
Doghouse: A small building on the rig floor which is used as the driller’s office. It also serves as a shelter for the drilling crew and storage for tools and small equipment.
BOP Stack: Stands for Blowout Preventer Stack. This piece of equipment is attached to the well head under the rig floor and utilizes vertically arranged closing elements to either close off the well or control the release of fluids to and from the well bore.
Cellar: A pit around the well head which provides space for the installation of equipment at the top of the well bore such as the BOP stack. Water and waste fluids also accumulate in the cellar for disposal.
Accumulator: A tank which holds hydraulic fluids stored under pressure by compressed nitrogen. An accumulator is used to actuate the blowout preventer.
SCR House/Top Drive: An electrical housing unit which balances and controls the energy used to power the top drive.
SCR House/Generator: An electrical housing unit in close proximity to the generator, which balances and controls the energy used to power the rig site. Also called a breaker house.
Engine/Generator Sets: Fueled most commonly by diesel, the engine converts fuel combustion into motion. The motion is then converted into electricity by the generator and is used as a power source for various drill site components.
Fuel Tank: Storage tanks that hold the diesel fuel used for the power system.
Water Tank: Stores water that is needed for various functions on the drill site, including circulating, cementing, cooling, and cleaning.
Mud Pumps: A set of two or three piston driven pumps that are used to move circulating fluids on a rotary drilling rig.
Mud System: The equipment that separates the earth cuttings coming out of the well bore and continues the circulating fluid back to the well bore.
Mud Pit: Also known as a reserve pit. An open excavation near the drilling rig that holds used or waste mud and cuttings.
Shale Shakers: A series of vibrating screens used to remove the earth cuttings from the circulating fluids from the well bore.
Mud/Gas Separator: A vessel that is attached to the mud flow line to remove gas from the circulated mud when drilling through a high-pressure gas zone.
Substructure: The steel platform and supports on which the mast and all drilling floor equipment sit. It also provides space for well control equipment and storage by elevating drilling floor components.
Mud Return Line: A pipe which carries the circulating drilling mud from the mud pumps to the well bore.
Choke Manifold: A series of pipes and valves that function to control pressures experienced during a kick once the blowout preventers are closed.
Catwalk: A long, flat steel platform where pipe is laid before it is pulled up through the V door and placed into the mousehole.
Pipe Racks with Drill Pipe: Steel platforms placed next to the rig near the catwalk that hold reserve drill pipe.
Company Man’s Quarters: The trailer in which the representative of the operator of the well offices and resides while on location.
Tool Pusher’s Quarters: The trailer in which the rig manager, also called rig superintendent or rig foreman, offices and resides while on location.
Rig Hands’ Quarters: The trailer in which the drilling crew resides when off duty.
Security Station: A structure at the entrance of the drilling location staffed by personnel that ensure controlled and authorized access to the site and enforces posted entrance requirements.
Sound Wall: Panels which can be installed on the perimeter of a well site to effectively reduce noise to the surrounding environment that is generated by drilling operations.
Other Educational Animations
Multi-stage Vertical Frac
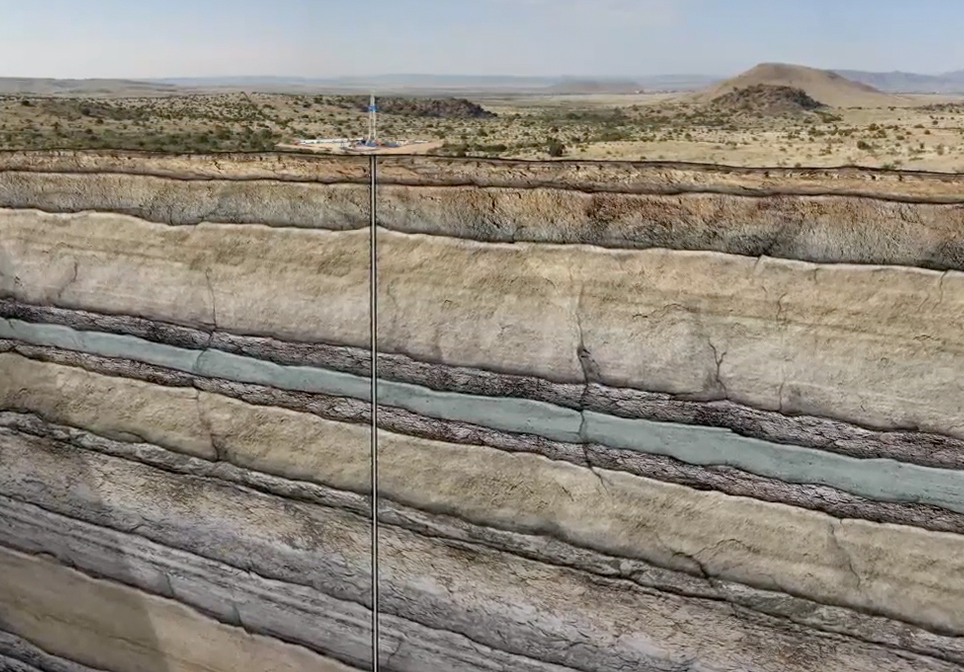

This Multi-Stage Vertical Frac Crude Oil Animation explains and demonstrates how a vertical well is drilled, stimulated and produced from multiple formations to recover hydrocarbons. In this animation, we show a well targeting three sandstone layers. The well is initially drilled to a designated distance below the deepest fresh water source near the surface.
Impact Crater
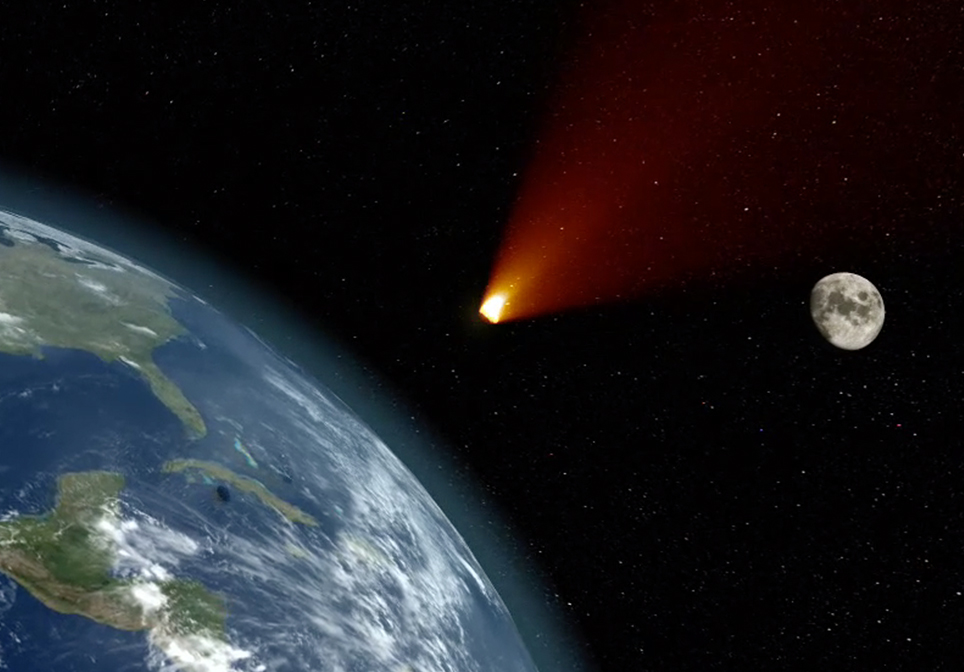

The 10 biggest impact craters on Earth date back from 35 million to over 2 billion years ago.
When an asteroid or meteorite crashes into the surface of a planet or a moon, a circular depression is formed. To form a true impact crater, this object needs to be traveling at super-fast speeds – many thousands of miles per hour! It immediately vaporizes and creates enormous shockwaves through the ground that melt and recrystallize rock and are one of the most destructive forces in the solar system.
The Chicxulub crater, sometimes referred to as the deadliest location on earth, is buried beneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. When the Chicxulub asteroid slammed into Earth about 66 million years ago, it obliterated 80 percent of Earth’s species, blasted out a crater about 200 kilometers (124 miles) across and 19 kilometers (12 miles) deep, and signaled an abrupt end to the Cretaceous Period.
CO2 EOR Carbon Dioxide Enhanced Oil Recovery
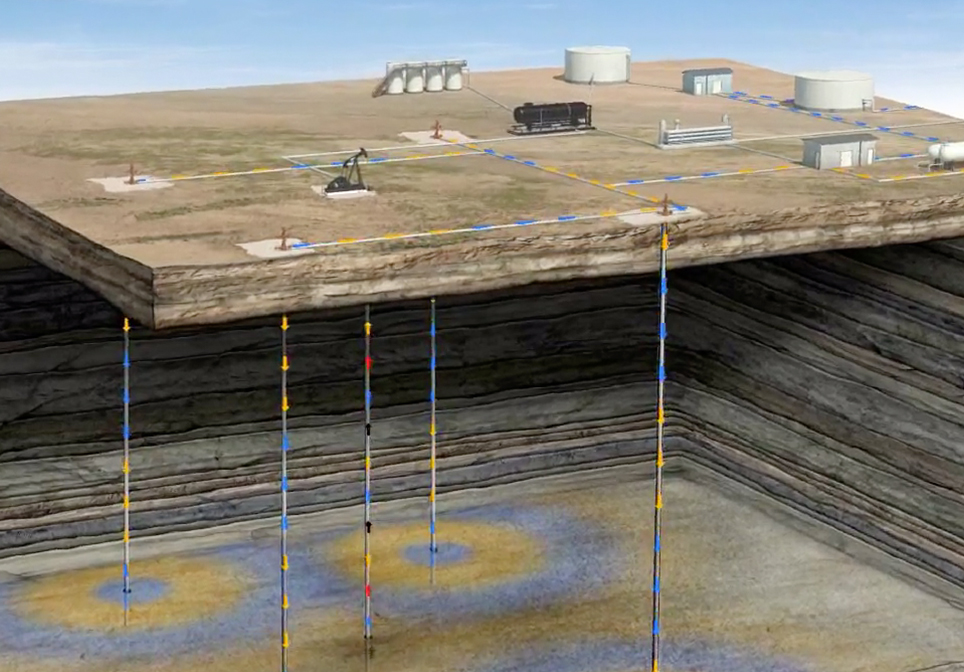
This CO2 EOR Educational Animation – created by John Perez Graphics & Design, LLC – explains the CO2-EOR process. We travel deep in to the Earth’s subsurface to demonstrate injection, miscibility, WAG, and increased oil production.
Saltwater Disposal
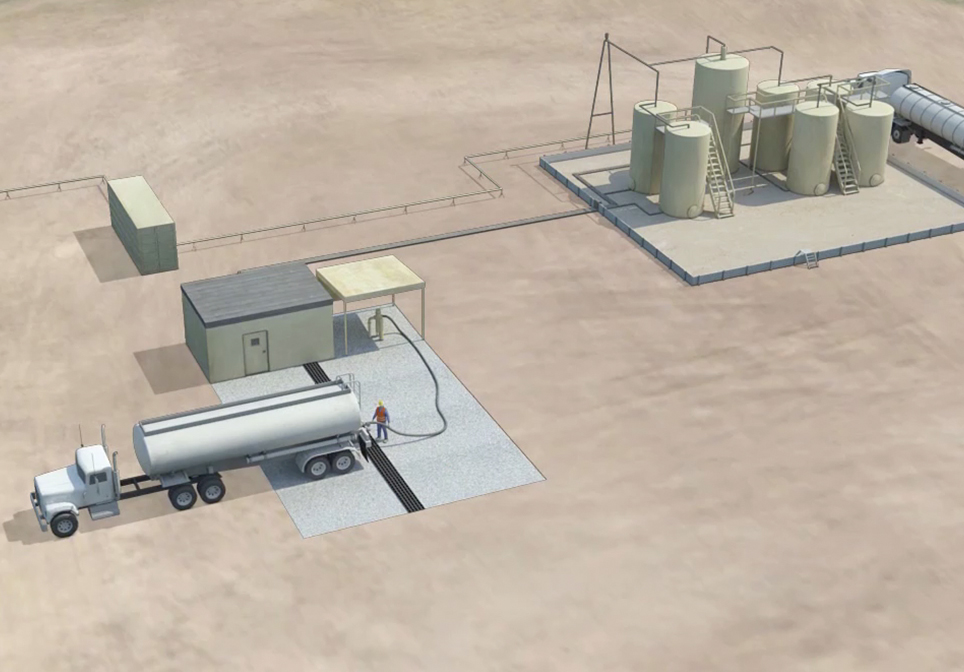

This Saltwater Disposal Well Animation – created by John Perez Graphics & Design, LLC – explains the steps necessary when disposing of salt water that is produced when drilling an oil or gas well. The animation takes you from the surface facilities, through the various protective casing strings down several thousand feet to the pre-approved formation zone where the salt water will be disposed of. This follows the EPA preferred method for the disposal of produced saltwater in Class II Saltwater Disposal wells.
